Teeth Whitening Effects The Ultimate Guide
Achieving a brighter, whiter smile is a common goal for many people, and with the myriad of teeth whitening options available, it’s more attainable than ever. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of teeth whitening, from understanding the causes of teeth discoloration to the different methods of whitening and how to maintain your results. Whether you’re considering professional treatments or exploring at-home solutions, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your dental health and aesthetic goals. We’ll delve into the science behind the procedures and offer advice to help you achieve the dazzling smile you’ve always desired.
Understanding Teeth Discoloration
Before diving into the world of teeth whitening, it’s crucial to understand what causes teeth to lose their natural brightness. Teeth discoloration can stem from various factors, and understanding these will help you determine the best approach for restoring your pearly whites. The color of our teeth is influenced by a combination of the enamel and the dentin beneath. The enamel, the hard outer layer, is translucent, allowing the color of the dentin to show through. As we age, the enamel thins, and the dentin, which naturally yellows over time, becomes more visible. This is just one piece of the puzzle when discussing the teeth whitening effects.
Causes of Teeth Discoloration
Teeth discoloration can be broadly categorized into extrinsic and intrinsic stains. Extrinsic stains affect the surface of the enamel, while intrinsic stains occur within the tooth structure.
Extrinsic Stains
Extrinsic stains are often caused by external factors such as consuming staining foods and drinks. These stains affect the enamel’s surface and are usually easier to remove with professional cleaning or at-home whitening products. Common culprits include coffee, tea, red wine, and certain foods like berries and curries. Smoking and tobacco use also contribute significantly to extrinsic staining, leading to a yellowish or brownish appearance. Fortunately, these stains are generally the easiest to address with teeth whitening methods.
Intrinsic Stains
Intrinsic stains originate from within the tooth structure, often resulting from factors like trauma, aging, certain medications, or excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development. These stains can be more challenging to remove as they’re embedded deep within the tooth. Tetracycline antibiotics, for example, can cause significant intrinsic staining if taken during tooth development. Similarly, injuries to the teeth can damage the nerves and blood supply, leading to discoloration. The treatment for intrinsic stains often requires more aggressive whitening techniques or alternative cosmetic procedures like veneers.
Factors Influencing Discoloration

Several lifestyle choices and biological processes influence the extent and rate of teeth discoloration. Understanding these factors will help you take preventive measures and make informed decisions about your oral care routine. The teeth whitening effects vary based on how these factors affect your teeth.
Dietary Habits
Your diet plays a significant role in the appearance of your smile. Consuming staining foods and beverages, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored fruits, can gradually darken your teeth. Frequent consumption of these items can lead to a quicker accumulation of extrinsic stains. The acidity of these substances can also erode enamel over time, making the teeth more susceptible to staining. Being mindful of your diet and practicing good oral hygiene can help mitigate these effects. Consider rinsing your mouth with water after consuming staining foods or drinks.
Oral Hygiene
The level of care you give your teeth directly impacts their color and overall health. Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can contribute to discoloration and make your teeth appear dull. Regular brushing removes surface stains, while flossing helps eliminate plaque and debris from hard-to-reach areas. Using a fluoride toothpaste and rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can further enhance your oral hygiene routine and contribute to maintaining a brighter smile. The teeth whitening effects are also based on good oral hygiene.
Ageing

As we age, our teeth naturally tend to darken. This is because the enamel, the outer protective layer, thins over time, allowing the yellow dentin underneath to become more visible. Additionally, years of consuming staining foods and drinks can accumulate, further contributing to discoloration. While ageing is a natural process, maintaining good oral hygiene and considering teeth whitening treatments can help counteract these effects and maintain a youthful, bright smile. Regular dental checkups are essential for monitoring the health of your teeth and addressing any age-related changes.
Teeth Whitening Methods
There are several methods available for whitening your teeth, each with its own advantages and considerations. The best method for you will depend on your individual needs, the severity of your staining, and your budget. Understanding the different options will help you choose the right approach for achieving your desired results. The teeth whitening effects will also be different in each method.
Professional Teeth Whitening
Professional teeth whitening, performed by a dentist, is often the most effective and quickest way to achieve a significantly brighter smile. These treatments use higher concentrations of whitening agents than over-the-counter products, delivering more dramatic results in a shorter amount of time. Professional whitening can be done in-office or at home, under the supervision of a dental professional. Consulting your dentist is crucial for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of any whitening procedure.
In-Office Whitening
In-office whitening involves a dentist applying a high-concentration whitening gel to your teeth. A special light or laser may be used to activate the whitening agent and accelerate the process. The entire procedure typically takes about an hour, and you can often see noticeable results immediately. Because of the strength of the whitening agents used, in-office treatments are often the most effective, particularly for severe staining. The dentist will also take measures to protect your gums and other soft tissues from irritation.
At-Home Whitening Kits
Your dentist can also provide custom-fitted trays and a professional-strength whitening gel for use at home. You wear the trays for a specified amount of time each day or night, following your dentist’s instructions. At-home whitening kits offer more control over the whitening process than in-office treatments, as you can adjust the frequency and duration of use to suit your needs. However, it’s still essential to follow your dentist’s instructions closely to minimize any risk of sensitivity or other side effects.
Over-the-Counter Whitening Products
If you’re looking for a more affordable and accessible option, over-the-counter (OTC) whitening products can be a good choice. These products typically contain lower concentrations of whitening agents than professional treatments, so they may take longer to produce visible results. Before using any over-the-counter whitening products, it’s important to consult your dentist, particularly if you have any existing dental issues. This consultation helps you understand potential risks and limitations and helps you choose the product that best fits your needs.
Whitening Toothpastes
Whitening toothpastes contain mild abrasives and/or chemicals that help remove surface stains. They can be an effective way to maintain the brightness of your teeth and remove extrinsic stains caused by foods and drinks. However, whitening toothpastes generally don’t change the intrinsic color of your teeth. Overuse of abrasive toothpastes can potentially wear down enamel, so it’s essential to use them as directed and consult with your dentist about their suitability for your teeth.
Whitening Strips
Whitening strips are thin, flexible strips coated with a whitening agent, usually hydrogen peroxide. They are applied directly to the teeth for a set period, according to the product instructions. Whitening strips can be effective in removing surface stains and providing noticeable results within a few weeks. They are easy to use and relatively inexpensive. However, they may not be suitable for all teeth, especially those with crowns, fillings, or other dental work. Be sure to follow the product’s instructions closely and discuss their use with your dentist.
The Science Behind Teeth Whitening
The teeth whitening process involves using chemical agents to break down the stain molecules embedded within the tooth enamel. Understanding the science behind the procedure will help you appreciate how the whitening agents work and why some methods are more effective than others.
How Whitening Agents Work
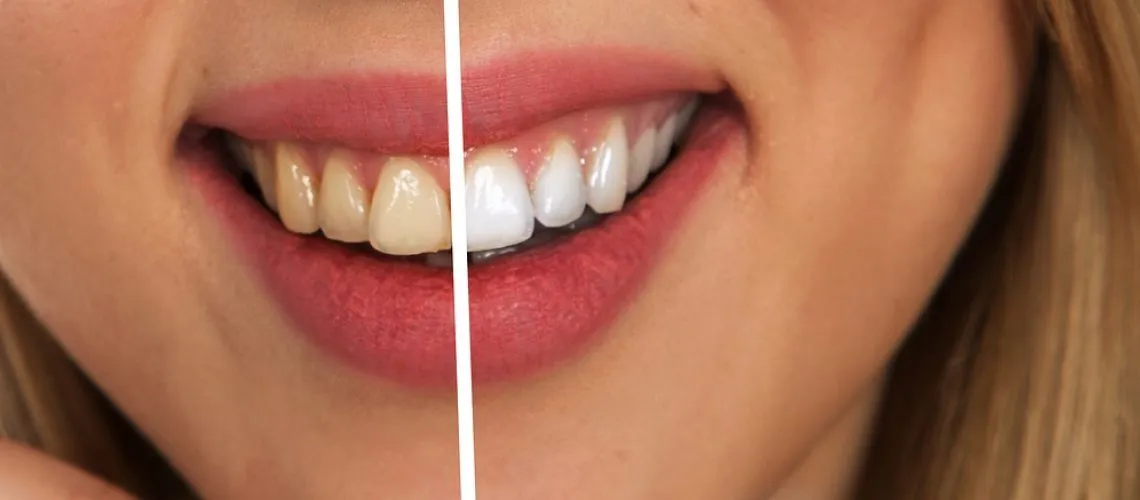
The active ingredient in most teeth whitening products is either hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These agents penetrate the enamel and dentin, breaking down the stain molecules. This process involves oxidation, where the peroxide molecules react with the stain molecules, breaking them into smaller, less visible components. The effectiveness of a whitening agent depends on its concentration and the duration of its contact with the teeth.
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a common whitening agent used in both professional and over-the-counter products. In the mouth, hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen. The oxygen molecules then react with the stain molecules within the tooth structure, effectively lightening the teeth. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide varies depending on the product, with professional treatments typically using higher concentrations than at-home kits.
Carbamide Peroxide
Carbamide peroxide is another widely used whitening agent. When it comes into contact with water, it breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea. The hydrogen peroxide then acts as the primary whitening agent. Carbamide peroxide is often used in at-home whitening kits because it releases hydrogen peroxide at a slower rate, which can reduce the risk of sensitivity. The urea component can also help hydrate the teeth, which can further reduce sensitivity.
Effectiveness and Limitations
The effectiveness of teeth whitening depends on several factors, including the type and severity of staining, the concentration of the whitening agent, and the duration of the treatment. Whitening is generally most effective on teeth with extrinsic stains, such as those caused by coffee, tea, or smoking. Intrinsic stains, such as those caused by tetracycline or fluorosis, may be more resistant to whitening and may require more aggressive treatments or alternative cosmetic procedures. Whitening treatments do not work on dental restorations like crowns, fillings, or veneers. These materials are not porous and cannot be whitened by the same methods that work on natural teeth. The teeth whitening effects may vary.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While teeth whitening is generally safe, there are potential side effects and risks associated with the procedure. Understanding these risks will help you make informed decisions about your treatment options and take steps to minimize potential complications. The teeth whitening effects have some side effects.
Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is one of the most common side effects of teeth whitening. It occurs because the whitening agents can penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin, where the tooth’s nerves are located. This can lead to temporary sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. The degree of sensitivity varies from person to person and depends on the concentration of the whitening agent and the duration of the treatment. Using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth before, during, and after treatment can help mitigate this side effect.
Gum Irritation
Gum irritation is another potential side effect, particularly with in-office whitening treatments, where the whitening agent is applied directly to the teeth. If the whitening agent comes into contact with the gums, it can cause irritation, redness, and soreness. This can be minimized by protecting the gums with a barrier during the procedure. At-home whitening kits can also cause gum irritation if the trays don’t fit properly, allowing the whitening gel to leak out. Proper fitting trays and following the dentist’s instructions are crucial to prevent this issue.
Enamel Damage
Although rare, there is a potential for enamel damage with excessive or improper use of teeth whitening products. Overuse of abrasive whitening toothpastes can wear down the enamel over time, making the teeth more susceptible to staining and sensitivity. Using professional whitening treatments too frequently or for extended periods can also potentially damage the enamel. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with your dentist to ensure your chosen method is safe and appropriate for your teeth. The teeth whitening effects may also cause this.
Maintaining Your White Smile
Once you’ve achieved your desired level of whiteness, it’s essential to take steps to maintain your results. This involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices, regular dental checkups, and mindful dietary choices. By adopting these habits, you can extend the lifespan of your brighter smile and prevent future discoloration.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is paramount for preserving your white smile. Brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time, using a fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and along the gum line. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacteria and promote oral health. A thorough oral hygiene routine helps prevent the buildup of stains and keeps your teeth looking their best. If you need any help in brushing your teeth, you can consult your dentist.
Regular Dental Checkups
Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings every six months to maintain your oral health and the appearance of your teeth. Your dentist can remove any surface stains, plaque, and tartar that you may have missed at home. During these visits, your dentist can also assess the health of your teeth and gums, identify any potential issues early on, and provide professional advice on maintaining your white smile. Regular dental visits are a cornerstone of preventative dental care.
Dietary Considerations
Be mindful of your diet to minimize the risk of future staining. Limit your consumption of staining foods and beverages such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored fruits. If you do consume these items, rinse your mouth with water immediately afterward or brush your teeth. Avoiding smoking and tobacco use can also help prevent discoloration. Choosing a diet rich in calcium and other nutrients essential for oral health will help keep your teeth healthy and strong, further enhancing the appearance of your smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about teeth whitening:
How long does teeth whitening last
The longevity of teeth whitening results varies depending on the method used, your oral hygiene habits, and your diet. Professional whitening treatments can last from several months to a few years. At-home whitening kits typically have shorter-lasting results. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding staining foods and beverages, and attending regular dental checkups can extend the lifespan of your white smile.
Is teeth whitening safe
Teeth whitening is generally safe when performed under the guidance of a dentist and when using approved products. However, there are potential side effects, such as sensitivity and gum irritation. Always follow the product instructions carefully and consult with your dentist before starting any whitening treatment to ensure it’s appropriate for your oral health and address any concerns you may have. Your dentist can also monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to minimize potential risks.
Who is a good candidate for teeth whitening
Most people with healthy teeth and gums are good candidates for teeth whitening. However, the best candidates have extrinsic stains or mild to moderate intrinsic stains. Individuals with sensitive teeth, gum disease, or other dental issues should consult with their dentist before whitening their teeth. Teeth whitening is not effective on dental restorations like crowns, fillings, and veneers. Your dentist can assess your suitability for teeth whitening based on your oral health and aesthetic goals.